lv shows concentric hypertrophy | left ventricular hypertrophy risk factors lv shows concentric hypertrophy Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart . See more Models from the Blossom, Empreinte and LV Volt collections are cast from 18-karat gold, enlivened with diamonds or colored gemstones. LOUIS VUITTON Official USA site - Shop designer bracelets from the iconic luxury brand. Discover women's and men's gold, silver, diamond bangles & leather bracelets.
0 · left ventricular hypertrophy risk factors
1 · left ventricular hypertrophy by voltage
2 · left ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure
3 · eccentric vs concentric hypertrophy heart
4 · concentric vs eccentric ventricular hypertrophy
5 · concentric vs eccentric lvh
6 · concentric vs eccentric hypertrophy causes
7 · concentric remodeling vs hypertrophy
They have the Sphere as a common drop (87% chance). Defender Z is encountered fairly often, and only requires you defeat him to get a sphere. Other ways to get Lv. 2 Key Spheres include finding them in various chests around Spira, as well as bribing Behemoths on Mt. Gagazet with 460,000 gil for x30 of the spheres.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is thickening of the walls of the lower left heart chamber. The lower left heart chamber is called the left ventricle. The left ventricle is the heart's main pumping chamber. During left ventricular hypertrophy, the thickened heart wall can become stiff. Blood pressure in the heart . See more
Left ventricular hypertrophy usually develops gradually. Some people do not have symptoms, especially during the early stages of the condition. Left ventricular hypertrophy itself doesn't cause symptoms. But symptoms may occur as the strain on the . See more
Anything that puts stress on the heart's lower left chamber can cause left ventricular hypertrophy. The lower left chamber is called the . See moreLeft ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart . See moreThings that increase the risk of left ventricular hypertrophy include: 1. Age.Left ventricular hypertrophy is more common in older people. So is . See more To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care .
left ventricular hypertrophy risk factors
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic .
Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is when the heart’s main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, becomes thicker and less able to pump blood efficiently. It usually develops .
In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling. In Part 2 of the blog we will elaborate on LV Mass (LVM) and Relative Wall Thickness . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to .
left ventricular hypertrophy by voltage
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a . If the wall thickness is seen involving all walls of the LV, it is considered to be concentric. If only some walls are involved, such as the septum, it is considered eccentric (eg, . Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood. To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope.
left ventricular hypertrophy and heart failure
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is when the heart’s main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, becomes thicker and less able to pump blood efficiently. It usually develops because of.In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling. In Part 2 of the blog we will elaborate on LV Mass (LVM) and Relative Wall Thickness (RWT).
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s conduction system that make it beat irregularly (arrhythmia).
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis. If the wall thickness is seen involving all walls of the LV, it is considered to be concentric. If only some walls are involved, such as the septum, it is considered eccentric (eg, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). Left ventricular hypertrophy changes the structure of the heart and how the heart works. The thickened left ventricle becomes weak and stiff. This prevents the lower left heart chamber from filling properly with blood.

To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Concentric left ventricular hypertrophy is an abnormal increase in left ventricular myocardial mass caused by chronically increased workload on the heart, most commonly resulting from pressure overload-induced by arteriolar vasoconstriction as occurs in, chronic hypertension or aortic stenosis. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is when the heart’s main pumping chamber, the left ventricle, becomes thicker and less able to pump blood efficiently. It usually develops because of.
eccentric vs concentric hypertrophy heart
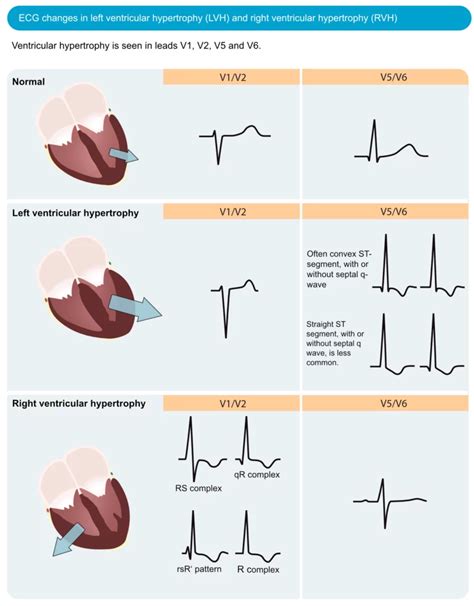
In this blog we describe left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and identify the different categories of concentric, eccentric and concentric remodeling. In Part 2 of the blog we will elaborate on LV Mass (LVM) and Relative Wall Thickness (RWT). Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) makes it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently. It can result in a lack of oxygen to the heart muscle. It can also cause changes to the heart’s conduction system that make it beat irregularly (arrhythmia).
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle.
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) refers to an increase in the size of myocardial fibers in the main cardiac pumping chamber. Such hypertrophy is usually the response to a chronic pressure or volume load. The two most common pressure overload states are systemic hypertension and aortic stenosis.
concentric vs eccentric ventricular hypertrophy
concentric vs eccentric lvh
Darbu uzsāk Uzdevumi.lv - izglītības portāls, kurā iespējams trenēties skolas mācību tēmās, kas atbilst Latvijas izglītības standartiem. 2010. Uzsākta savstarpēja sadarbība ar skolvedības sistēmu E-klase. 2014. Darbu uzsāk Uzdevumi.lv jaunā versija - vēl izskatīgāk, vēl kvalitatīvāk un vēl parocīgāk. 2016
lv shows concentric hypertrophy|left ventricular hypertrophy risk factors