lv wall stress | laplace law heart lv wall stress After adjustment for age, arterial properties, end-diastolic LV geometry, and cardiac output, women demonstrated greater peak, average systolic, and end-systolic wall stress than . Penn Praxis is a Design Partner with the Lehigh Valley Planning Commission, along with a team of Design Fellows, to design a 25-year plan for the region called Future LV for ecological health and quality .
0 · what is myocardial oxygen tension
1 · wall tension vs stress
2 · stress Lv end systolic volume
3 · myocardial wall tension
4 · myocardial wall stress results
5 · law of laplace cardiology
6 · laplace's theory of wall tension
7 · laplace law heart
Thanks to a major comeback on the runways, designers like Louis Vuitton, Fendi, and Bottega Veneta have catapulted the fanny pack, or the more fashionable monitor "belt bag," to cool-girl.
what is myocardial oxygen tension
Ventricular wall stress (WS) is an important hemodynamic parameter to represent myocardial oxygen demand and ventricular workload. The normalization of WS is regarded as a physiological feedback signal that regulates the rate and extent of ventricular hypertrophy to maintain . After adjustment for age, arterial properties, end-diastolic LV geometry, and cardiac output, women demonstrated greater peak, average systolic, and end-systolic wall stress than .
wall tension vs stress
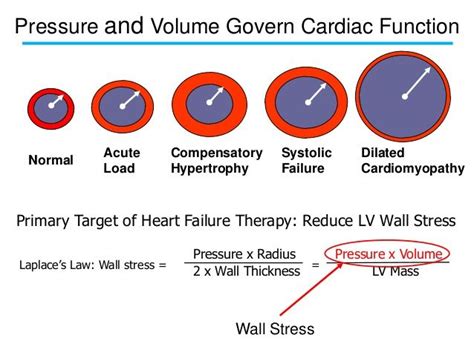
The afterload on individual muscle fibers within the wall of the heart is often expressed as ventricular wall stress (σ) and described by the following equation: (P, ventricular pressure; r, ventricular radius; h, wall thickness).
In the presence of normal LV ejection fraction, a midsystolic shift in the pressure-stress relationship protects cardiomyocytes against excessive late systolic stress (despite pressure augmentation associated with wave .
LV end systolic and diastolic wall stress (LVESWS, LVEDWS) were calculated at baseline among 4,601 ARIC study participants without prevalent HF. LVEDWS, but not LVESWS, was .
We detected significantly reduced rates of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in association with lower LV mass×wall stress×heart rate products in a population of hypertensive patients with ECG LVH who had not .
This paper can enable readers to obtain a comprehensive perspective of left ventricle wall stress models, of how to employ them to determine wall stresses, and be .We characterized left ventricular wall stress (LVWS) profiles in pressure and volume-overloaded systems, examined the relationship between baseline LVWS and cardiac remodeling, and .
Wall stress is a useful concept to understand the progression of ventricular remodeling. We measured cumulative LV wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle over unit time and tested .
stress Lv end systolic volume
As myocardial energetics can be impaired during AS, LV wall stresses and biomechanical power provide a complementary view of LV performance that may aide in better .Ventricular wall stress (WS) is an important hemodynamic parameter to represent myocardial oxygen demand and ventricular workload. The normalization of WS is regarded as a physiological feedback signal that regulates the rate and extent of ventricular hypertrophy to maintain myocardial homeostasis. After adjustment for age, arterial properties, end-diastolic LV geometry, and cardiac output, women demonstrated greater peak, average systolic, and end-systolic wall stress than men, possibly accounting for greater predisposition to heart failure, particularly heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, in women compared with men.The afterload on individual muscle fibers within the wall of the heart is often expressed as ventricular wall stress (σ) and described by the following equation: (P, ventricular pressure; r, ventricular radius; h, wall thickness).

In the presence of normal LV ejection fraction, a midsystolic shift in the pressure-stress relationship protects cardiomyocytes against excessive late systolic stress (despite pressure augmentation associated with wave reflections), a coupling mechanism that may be altered in various disease states.LV end systolic and diastolic wall stress (LVESWS, LVEDWS) were calculated at baseline among 4,601 ARIC study participants without prevalent HF. LVEDWS, but not LVESWS, was associated with the risk of incident heart failure over a median follow-up of 4.6 years. We detected significantly reduced rates of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in association with lower LV mass×wall stress×heart rate products in a population of hypertensive patients with ECG LVH who had not only increased LV mass but also increased substantially supranormal wall stresses and even more markedly elevated triple .
This paper can enable readers to obtain a comprehensive perspective of left ventricle wall stress models, of how to employ them to determine wall stresses, and be cognizant of the assumptions involved in the use of specific models.
We characterized left ventricular wall stress (LVWS) profiles in pressure and volume-overloaded systems, examined the relationship between baseline LVWS and cardiac remodeling, and assessed the acute effects of valve intervention on LVWS using invasive pressures combined with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging measures of left ventricular .
Wall stress is a useful concept to understand the progression of ventricular remodeling. We measured cumulative LV wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle over unit time and tested whether this “integrated wall stress (IWS)” would provide a . As myocardial energetics can be impaired during AS, LV wall stresses and biomechanical power provide a complementary view of LV performance that may aide in better assessing the state of disease. Objectives.Ventricular wall stress (WS) is an important hemodynamic parameter to represent myocardial oxygen demand and ventricular workload. The normalization of WS is regarded as a physiological feedback signal that regulates the rate and extent of ventricular hypertrophy to maintain myocardial homeostasis. After adjustment for age, arterial properties, end-diastolic LV geometry, and cardiac output, women demonstrated greater peak, average systolic, and end-systolic wall stress than men, possibly accounting for greater predisposition to heart failure, particularly heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, in women compared with men.
The afterload on individual muscle fibers within the wall of the heart is often expressed as ventricular wall stress (σ) and described by the following equation: (P, ventricular pressure; r, ventricular radius; h, wall thickness). In the presence of normal LV ejection fraction, a midsystolic shift in the pressure-stress relationship protects cardiomyocytes against excessive late systolic stress (despite pressure augmentation associated with wave reflections), a coupling mechanism that may be altered in various disease states.
LV end systolic and diastolic wall stress (LVESWS, LVEDWS) were calculated at baseline among 4,601 ARIC study participants without prevalent HF. LVEDWS, but not LVESWS, was associated with the risk of incident heart failure over a median follow-up of 4.6 years. We detected significantly reduced rates of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in association with lower LV mass×wall stress×heart rate products in a population of hypertensive patients with ECG LVH who had not only increased LV mass but also increased substantially supranormal wall stresses and even more markedly elevated triple . This paper can enable readers to obtain a comprehensive perspective of left ventricle wall stress models, of how to employ them to determine wall stresses, and be cognizant of the assumptions involved in the use of specific models.We characterized left ventricular wall stress (LVWS) profiles in pressure and volume-overloaded systems, examined the relationship between baseline LVWS and cardiac remodeling, and assessed the acute effects of valve intervention on LVWS using invasive pressures combined with cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging measures of left ventricular .
swatch omega sale shop
Wall stress is a useful concept to understand the progression of ventricular remodeling. We measured cumulative LV wall stress throughout the cardiac cycle over unit time and tested whether this “integrated wall stress (IWS)” would provide a .
myocardial wall tension
myocardial wall stress results
law of laplace cardiology
Louis Vuitton Belt Bags & Fanny Packs for Women. All. Auction. Buy It Now. Best Match. 11 Results. 3 filters applied. Style. Brand. Finish. Exterior Color. Size. Condition. Buying Format. Delivery Options. All Filters. Authentic LOUIS VUITTON Taiga rama Bum bag outdoor M30430 Shoulder bag #270-. $1,143.75. $35.00 shipping. Authenticity Guarantee.100% Polyester. Black. LOUIS VUITTON Official USA site - Discover our latest Mesh Shorts, available exclusively on louisvuitton.com and in Louis Vuitton stores.
lv wall stress|laplace law heart