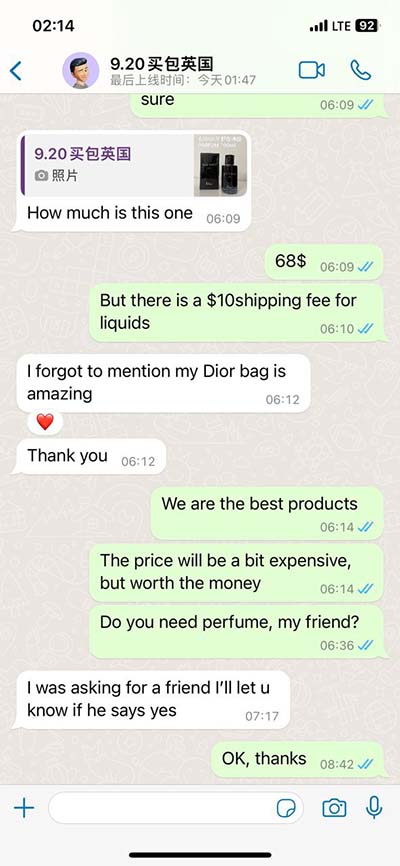
lv wall thickness | left ventricle increased wall thickness lv wall thickness Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass.
Drošs, vieds un ērti lietojams e-pasts. Paveiciet vairāk, izmantojot Gmail. Tagad tas ir integrēts ar Google Chat, Google Meet un citiem pakalpojumiem — viss pieejams vienuviet. Izveidot.
0 · lv wall thickness on echo
1 · lv wall thickness normal values
2 · lv wall thickness normal range
3 · lv wall thickness calculator
4 · left ventricular wall thickness women
5 · left ventricular wall thickness chart
6 · left ventricle increased wall thickness
7 · heart wall thickness chart
Low voltage switchgear uses various components to ensure safe maintenance, protect circuits, and deliver electricity. Typical applications for low voltage switchgear include air conditioners and heaters, motors, compressors, lighting networks, and many more. Main Components of Low Voltage Switchgear.
lv wall thickness on echo
chanel tote quilted
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic . Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which an increase in left ventricular mass occurs secondary to an increase in wall thickness, an increase in left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both. Learn about the causes, symptoms and diagnosis of left ventricular hypertrophy, a condition that thickens the heart muscle. Find out how to treat it with medicines, surgery or .
Left ventricular hypertrophy is thickening of the walls of the left ventricle, the heart’s main chamber. The left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta (the largest artery in the .
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic . LVH is when the left ventricle of the heart becomes thicker and less efficient due to another heart condition. Learn about the risk factors, diagnosis, and management of LVH and .When you have LVH, the muscle wall of the left ventricle becomes thick (hypertrophy) and enlarged. LVH can happen over time if you have certain health conditions that overwork the .
Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which an increase in left ventricular mass occurs secondary to an increase in wall thickness, an increase in left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both.
lv wall thickness normal values
To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope. Left ventricular hypertrophy is thickening of the walls of the left ventricle, the heart’s main chamber. The left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta (the largest artery in the body), which sends this oxygenated blood to tissues throughout your body.Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. In response to this pressure overload, the inner walls of the heart may respond by getting thicker.
When a condition causes the heart to work harder to supply the body with oxygenated blood, the left ventricle walls can become thicker — similar to how other muscles can become bigger from.
When you have LVH, the muscle wall of the left ventricle becomes thick (hypertrophy) and enlarged. LVH can happen over time if you have certain health conditions that overwork the heart muscle, such as high blood pressure or aortic stenosis. As the heart works harder than normal, the left ventricle adapts. Left ventricular hypertrophy is a thickening of the wall of the heart's main pumping chamber, called the left ventricle. This thickening may increase pressure within the heart. The condition can make it harder for the heart to pump blood.
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. Increased left ventricular myocardial thickness (LVMT) is a feature of several cardiac diseases. The purpose of this study was to establish standard reference values of normal LVMT with cardiac magnetic resonance and to assess variation with image acquisition plane, demographics, and left ventricular function. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is a condition in which an increase in left ventricular mass occurs secondary to an increase in wall thickness, an increase in left ventricular cavity enlargement, or both. To diagnose left ventricular hypertrophy, a healthcare professional does a physical exam and asks questions about your symptoms and family's health history. The care professional checks your blood pressure and listens to your heart with a device called a stethoscope.
Left ventricular hypertrophy is thickening of the walls of the left ventricle, the heart’s main chamber. The left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta (the largest artery in the body), which sends this oxygenated blood to tissues throughout your body.Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass.
Left ventricular hypertrophy, or LVH, is a term for a heart’s left pumping chamber that has thickened and may not be pumping efficiently. Sometimes problems such as aortic stenosis or high blood pressure overwork the heart muscle. In response to this pressure overload, the inner walls of the heart may respond by getting thicker. When a condition causes the heart to work harder to supply the body with oxygenated blood, the left ventricle walls can become thicker — similar to how other muscles can become bigger from.


Oops, something went wrong. Find a Location; Franchise; About; Charity; Spain; Find a Location Franchise
lv wall thickness|left ventricle increased wall thickness